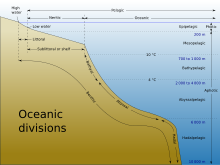
The abyssal zone is the abyssopelagic layer or pelagic zone that contains the very deep benthic communities near the bottom of oceans. "Abyss" derives from the Greek word ἄβυσσος, meaning bottomless. At depths of 4,000 to 6,000 metres (13,123 to 19,685 feet), this zone remains in perpetual darkness and never receives daylight. These regions are also characterised by continuous cold and lack of nutrients. The abyssal zone has temperatures around 2 °C to 3 °C (35 °F to 37 °F) through the large majority of its mass. It is the deeper part of the midnight zone which starts in the bathypelagic waters above. Its permanent inhabitants (for example, Riftia pachyptila, (the Giant tube worm) found near hydrothermal vents in the pacific ocean) are able to withstand the immense pressures of the ocean depths, up to 76 megapascals (11,000 psi).
The area below the abyssal zone is the sparsely inhabited Hadal zone. The zone above is the bathyal zone. These three zones belong to the deep-sea realm. Above on the continental platform there are respectively the euphotic and dysphotic zones. The abyssal zone lies partially in the dysphotic and partially in the aphotic zones.
Trenches

The deep trenches or fissures that plunge down thousands of metres (feet) below the ocean floor (for example, the midoceanic trenches such as the Mariana Trench in the Pacific) are almost unexplored. Previously, only the bathyscaphe Trieste, the remote control submarine Kaiko and the Nereus have been able to descend to these depths. However, as of March 25, 2012 one vehicle, the Deepsea Challenger was able to penetrate to a depth of 10,898.4 metres (35,756Â ft).
See also
- Abyssal plain
- Deep sea
- Mariana Trench
References

